A Guide to Implementing ISO 27001
In a world increasingly driven by digital information, ensuring the security of sensitive data is crucial. ISO 27001:2022 is the international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), providing a comprehensive framework to safeguard against security threats. Implementing this standard is no small task, but the benefits are extensive - improving operational efficiency, reducing risks, and enhancing customer trust.
Read on as we explore the essentials of ISO 27001, and outline our ISO 27001 Implementation Guide's critical sections, offering a roadmap for those embarking on the ISO 27001 journey.
Why ISO 27001 matters
Information security breaches can have devastating consequences, from financial losses to reputational damage. ISO 27001 helps your organisation proactively manage risks by establishing a robust ISMS. This standard has become a critical tool and demonstrates your commitment to security and gain a competitive edge.
A brief history of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is part of the ISO 27000 series, a collection of standards designed to address various aspects of information security. It originated from the UK's BS 7799 in 1995 and is jointly maintained by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Since its inception, ISO 27001 has undergone several revisions, with the latest update in 2022.
Benefits of implementing ISO 27001
By achieving ISO 27001 certification your organisation can enjoy several benefits:
Commercial advantage: certification can set your business apart, providing a competitive edge when bidding for contracts or attracting customers.
Operational efficiency: ISO 27001 fosters a culture of security awareness, leading to consistent and effective risk management practices.
Regulatory compliance: certification can demonstrate compliance with data protection laws, reducing the risk of legal penalties.
What is inside the ISO 27001 Implementation Guide?
The PDF guide for implementing ISO 27001 is valuable for organisations seeking certification. Here's an overview of its key sections:
Key principles and terminology
This section covers the fundamental concepts and terminology used in ISO 27001, such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, incidents, and threats. Understanding these terms is essential for navigating the standard.
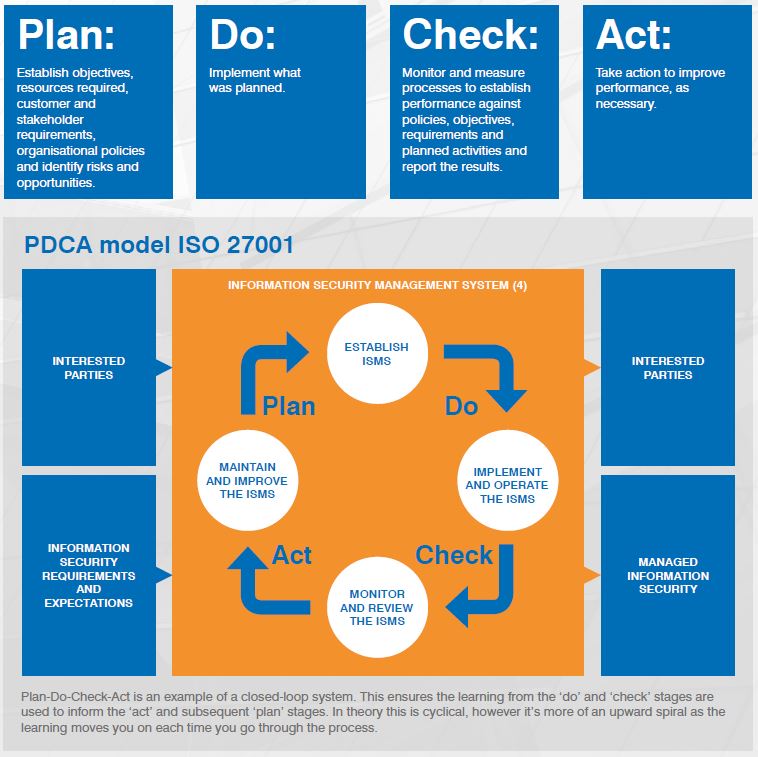
PDCA Cycle
ISO 27001 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, the Deming wheel or the Shewhart cycle. The PDCA cycle can be applied to the management system as a whole and encourages continuous improvement by guiding organisations through planning, implementing, reviewing, and refining their ISMS.
Risk - based and process - based thinking / audits
Risk-based thinking focuses on identifying and mitigating risks, while process-based thinking examines the efficiency and effectiveness of various processes.
Audits are a systematic, evidence-based, process approach to evaluation of your Information Security Management System. They are undertaken internally and externally to verify the effectiveness of the ISMS. Audits are a brilliant example of how risk-based thinking is adopted within Information Security Management.
You should establish a risk assessment method and a treatment plan, including guidelines for acceptable risks and criteria to conduct risk assessments. This approach should be seamlessly integrated into your management system. Risks should be prioritised and addressed accordingly.
A process is the transformation of inputs to outputs, the process is a series of steps or activities which result in the planned objective(s). Often the output of one process becomes an input to another subsequent process. Very few processes operate in isolation from any other.
Understanding how processes interrelate and produce results can help you identify opportunities for improvement and optimise overall performance. This also applies where processes, or parts of processes, are outsourced.
To understand the various types of audits, read the full Implementation Guide.
Annex SL
Annex SL is the structure of ISO 27001, which aligns with other ISO standards like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System) and ISO 45001 (Health and Safety Management System). Before the adoption of Annex SL, there were many differences between the clause structures, requirements and terms and definitions used across the various management system standards. By introducing Annex SL there is now a common structure that facilitates easier integration of multiple standards within an organisation.
Annex SL consists of 10 core clauses:
-
Scope: defines the standard's scope and application.
-
Normative references: lists other ISO standards referenced.
-
Terms and definitions: provides specific definitions for terms used in the standard.
-
Context of the organisation: outlines the importance of understanding the organisation's internal and external context.
-
Leadership: highlights the importance of leadership in supporting the ISMS.
-
Planning: focuses on risk assessment and treatment.
-
Support: covers resources, competence, and communication.
-
Operation: details of how the ISMS is implemented and managed.
-
Performance evaluations: addresses monitoring, measurement, and audits.
-
Improvement: discusses corrective actions and continuous improvement.
ISO 27001:2022 clauses
Like many ISO management system standards, the requirements for ISO 27001 need to be satisfied within the 10 Clauses of Annex SL. Unlike other system standards, ISO 27001 requires you must comply with all requirements, you cannot declare one or more clauses are not applicable.
In addition, ISO 27001 has a set of requirements detailed in Annex A, which is referenced in Clause 6.
Annex A
ISO 27001 follows a risk-based approach when considering the information security of an organisation. This requires the identification of security risks and then the selection of appropriate controls to reduce, eliminate, or manage those risks.
When conducting the risk process, the risk identified should have appropriate controls that have been selected from the list in Annex A. Annex A contains 93 information security controls. Each of these 93 controls needs to be considered. There are four key categories of controls:
-
Organisation controls
-
People controls
-
Physical controls
-
Technological controls
To be compliant with ISO 27001, your organisation must implement these controls, or an acceptable justification must be given for not implementing a particular control.
Next steps once implemented
The journey doesn't end with ISO 27001 certification. This section guides maintaining and improving your ISMS, emphasising the importance of ongoing vigilance and adaptation to evolving security threats.
NQA's final thoughts
Reading our Implementation Guide can better prepare for ISO 27001 implementation and certification. The complete PDF guide offers detailed information, making it an indispensable resource for those committed to achieving and maintaining high information security standards.
Download the full ISO 27001:2022 Implementation Guide here.
![]() Want to gain more knowledge on ISO 27001:2022? Explore our latest training!
Want to gain more knowledge on ISO 27001:2022? Explore our latest training!
![]() Confident in ISO 27001:2022? Contact our friendly sales team to discuss how we can support you.
Confident in ISO 27001:2022? Contact our friendly sales team to discuss how we can support you.

